Visual Capitalist |
| The Most Significant Cyber Attacks from 2006-2020, by Country Posted: 10 May 2021 05:01 PM PDT
The Briefing
Significant Cyber Attacks from 2006-2020, by CountryCommitting a cyber crime can have serious consequences. In the U.S., a cyber criminal can receive up to 20 years in prison for hacking into a government institution if it compromises national security. Yet, despite the consequences, cyber criminals continue to wreak havoc across the globe. But some countries seem to be targeted more than others. Using data from Specops Software, this graphic looks at the countries that have experienced the most significant cyber attacks over the last two decades.
The U.S. comes in first place, with 156 recorded cyber attacks. That's an average of 11 significant attacks per year, which is more than Russia's had in 14 years. What are the Most Common Types?While there are many different types of cyber attacks, Specops highlights the four most commonly used for significant cyber crimes:
»Like this? Here's another article you might enjoy: The 15 Biggest Data Breaches in the Last 15 Years Where does this data come from? Source: Specops Software The post The Most Significant Cyber Attacks from 2006-2020, by Country appeared first on Visual Capitalist. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Canada’s Gold Exploration Frontier: The Abitibi Greenstone Belt Posted: 09 May 2021 11:12 PM PDT The following content is sponsored by Maple Gold Mines. 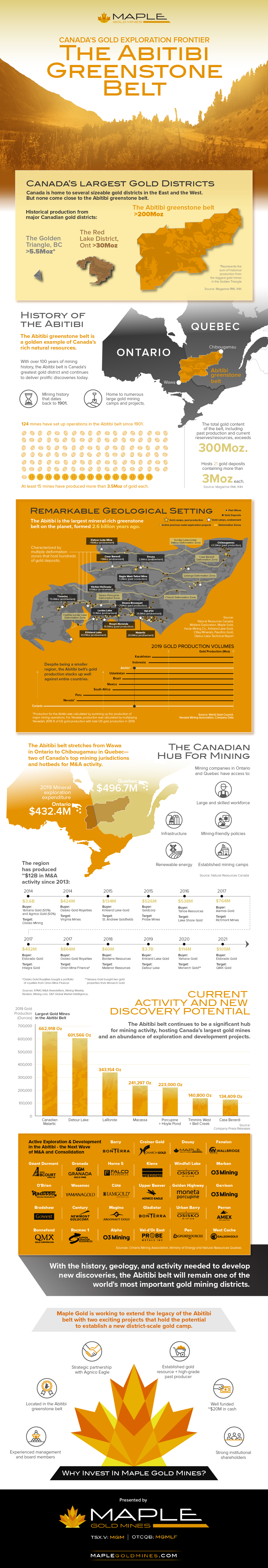 The Abitibi: Canada's Largest Gold DistrictCanada is home to many great gold districts, but none come close to the Abitibi greenstone belt. Having produced over 200 million ounces of gold since 1901, the Abitibi belt has etched its place as Canada's largest gold district. Today, the region is bustling with exploration activity and hosts three of the country's largest gold mines. The above infographic from Maple Gold Mines showcases what makes the Abitibi a prolific gold district, from its history and geology to current activity and the potential for discovery. The Abitibi Greenstone Belt: Remarkable Geology and HistoryOver 2.6 billion years ago, the Earth's natural processes of creation and destruction resulted in the formation of metal-rich volcanic rocks and deformation zones that comprise the Abitibi greenstone belt. The Abitibi belt hosts several economically viable deposits of gold, silver, zinc, iron, copper, and other base metals. The types of deposits found there include gold-rich quartz-carbonate veins, copper porphyries, and volcanogenic massive sulfide (VMS) deposits. Since mining began in the early 1900s, more than 124 mines have been set up in the Abitibi, and at least 15 of these have yielded over 3.5 million ounces of gold. What's more, the total gold content of the belt, including past production and current reserves and resources, exceeds 300 million ounces. The majority of the Abitibi's rich gold deposits lie along fault lines in major deformation zones such as the Cadillac-Larder Lake zone and the Destor-Porcupine zone. These deposits are the foundations of gold camps that boast historical production numbers in excess of 10 million ounces of gold. Despite a mining history that spans over 100 years, the Abitibi belt remains an active mining region with plenty of potential for new discoveries. Mining Activity and the Potential for DiscoveryWith one end in Wawa, Ontario, and the other in Chibougamau, Quebec, the Abitibi's location spans two jurisdictions that offer various advantages for mining companies. Ontario and Quebec are two of Canada's top mining jurisdictions with 2019 exploration expenditures of $432.4 million and $496.7 million, respectively. Mining companies in the Abitibi benefit not only from its rich resource endowment but also from the infrastructure, skilled workforces, and mining-friendly policies in its jurisdictions. In fact, the Abitibi has produced around $12 billion in mining M&A transactions since 2013.
*Osisko Gold Royalties bought a portfolio of royalties from Orion Mine Finance and Yamana Gold bought two properties from Monarch Gold. Back in 2014, Yamana Gold and Agnico Eagle each bought a 50% stake in Osisko Mining for a total of $3.6 billion to own Osisko's flagship Canadian Malartic Mine, Canada's largest gold mine. In a similarly-sized transaction in 2019, Kirkland Lake Gold acquired the Detour Lake mine—the second-largest gold mine in the country, for $3.7 billion. Both of these mines share a common home—the Abitibi greenstone belt. The Legacy ContinuesThe Abitibi belt remains a hub for mining activity with Canada's largest gold mines and 28 exploration projects on the hunt for precious metals and the next wave of M&A transactions. With its rich history, remarkable geology, and plenty of gold left to discover, the Abitibi greenstone belt's legacy as one of the world's most important gold districts will continue. The post Canada’s Gold Exploration Frontier: The Abitibi Greenstone Belt appeared first on Visual Capitalist. |
| You are subscribed to email updates from Visual Capitalist. To stop receiving these emails, you may unsubscribe now. | Email delivery powered by Google |
| Google, 1600 Amphitheatre Parkway, Mountain View, CA 94043, United States | |
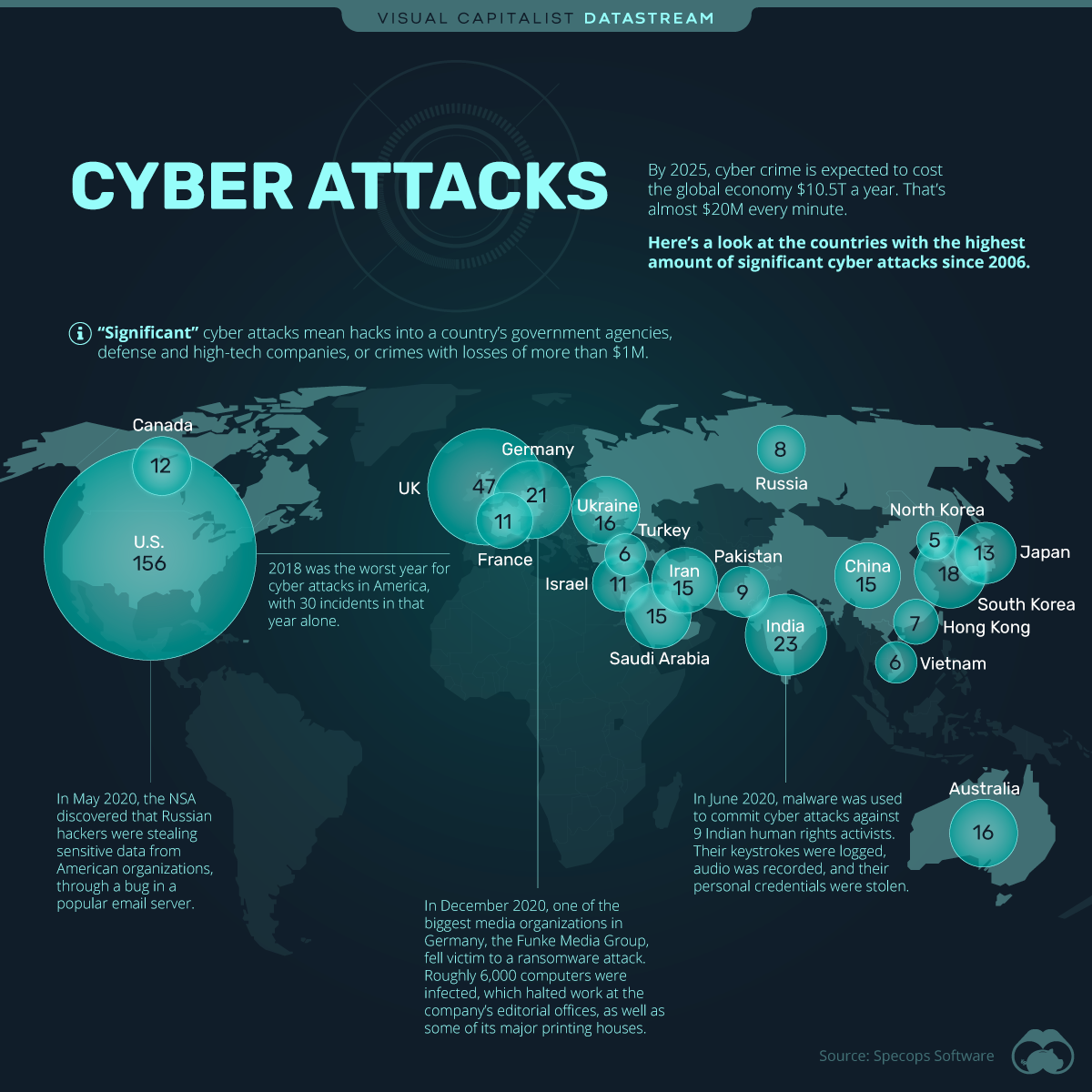



 United States
United States United Kingdom
United Kingdom India
India Germany
Germany South Korea
South Korea Australia
Australia Ukraine
Ukraine China
China Iran
Iran Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia Japan
Japan Canada
Canada France
France Israel
Israel Pakistan
Pakistan Russia
Russia Hong Kong
Hong Kong Vietnam
Vietnam Turkey
Turkey North Korea
North Korea
No comments:
Post a Comment